

Install swales and drains and grade the site to control stormwater runoff on site and to prevent soil saturation around the foundation.
See the Compliance tab for related codes and standards requirements, and criteria to meet national programs such as DOE’s Zero Energy Ready Home program, ENERGY STAR Single-Family New Homes, and Indoor airPLUS.
Description DescriptionA few inches of rain falling on a typical suburban lot can produce 9,750 gallons of water runoff (HUD 2019, EPA 2018). This runoff must be channeled away from the building foundation to keep the basement or crawlspace dry and to prevent water from seeping into the building interior where it may create moisture problems. Water management is an important part of the design and construction of the home. Keeping water from entering the house is critical to ensuring the long-term structural integrity of the building. Water saturation of foundations and siding can lead to mold problems, as well as poor indoor air quality.
The ground around the house should be graded to slope away from the house, as described in the Building America Solution Center guides Final Grade Slopes Away from Foundation and Patio Slabs, Porch Slabs, Walks, and Driveways Slope Away from House. Other solutions are available for sites that are level or that have unavoidable slope toward the house. Or, if there are municipal requirements in place to retain stormwater runoff on site. Swales can be constructed to provide a means to drain stormwater from the site’s surface. Drains can also be installed to handle higher volumes of surface water. More information about onsite water drainage can also be found in the Solution Center guide Gutters and Downspouts. Information about minimizing erosion on site can be found in the guide Erosion Control for Slopes, Stream Banks, and Dunes.
Swales
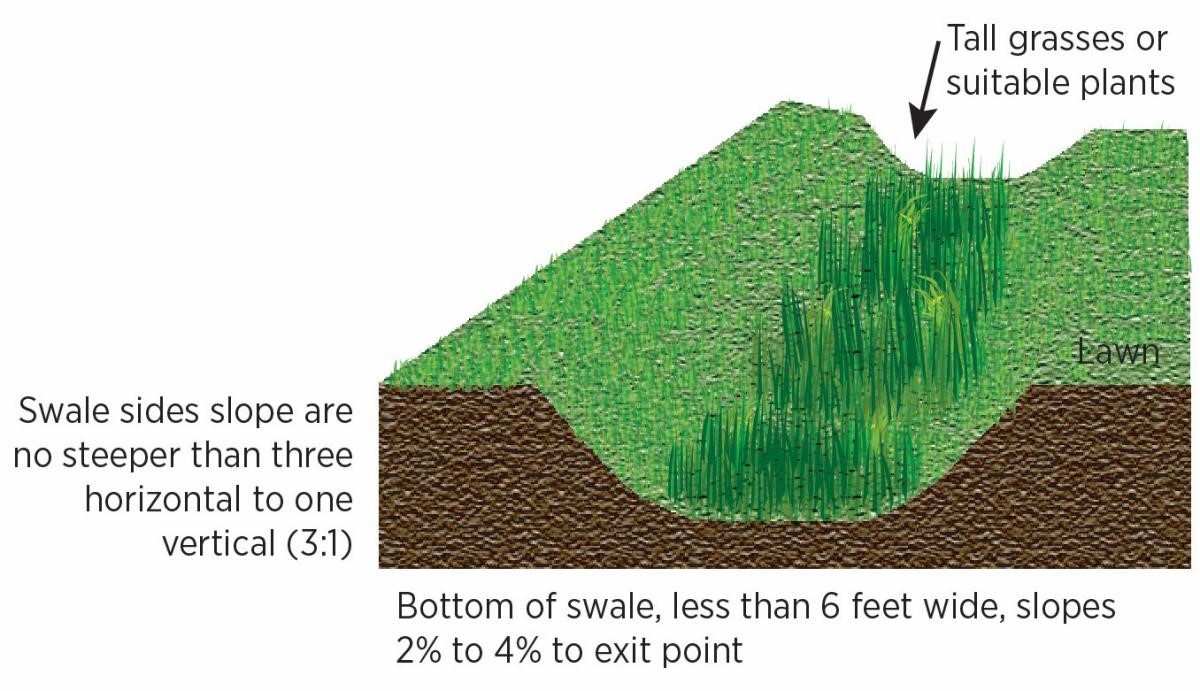
A swale is a trapezoidal channel that is dug to receive storm water overflow, allowing it a path to flow away from the home (Figure 1). Swales can provide a means to slow water runoff and allow natural percolation into the soil on site. They are typically located along property boundaries or at the base of a natural grade. They will also draw in water that would otherwise sit in a flat yard and they can divert water flowing toward the house from an upward sloping yard. Swales are typically planted with specific types of vegetation to reduce erosion, to help remove any pollutants found in the storm water runoff, and to improve the aesthetics of the design.

The installed vegetation should adequately remove and retain heavy metals. Examples of vegetation appropriate for use in swales include reed canary grass, grass-legume mixtures, and red fescue. The swale should be large enough to comfortably divert the volume of precipitation (rain fall or snowmelt runoff) expected for a 6-month-frequency, 24-hour storm event. The sides of the swale should have a slope no steeper than 3 to 1, and the first 8 inches of the soil should drain well (Figure 2) (Enterprise Communities 2019).
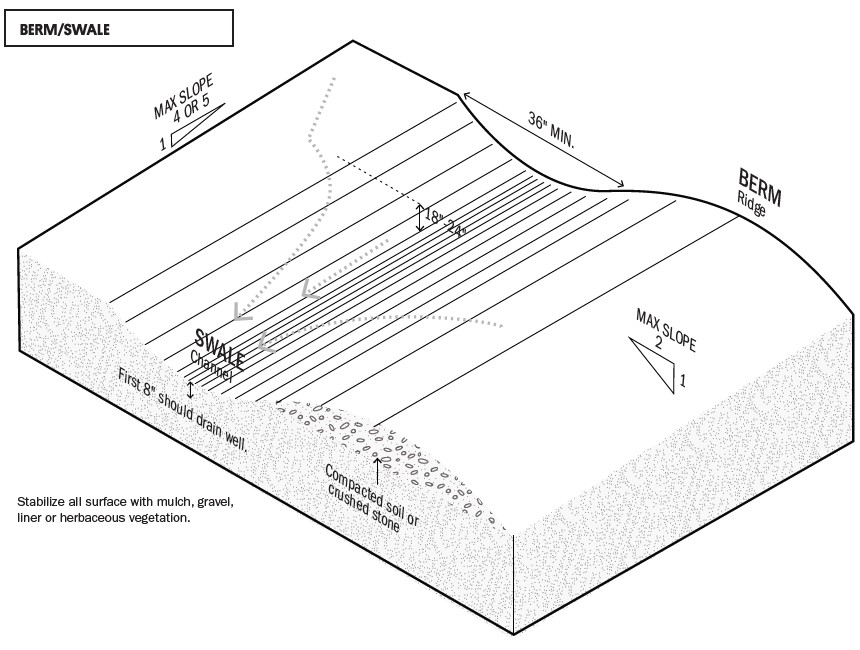
Swales can be installed in combination with berms across slopes to slow the descent of stormwater and reduce erosion (Figure 3). For faster drainage where large water volumes are expected, a French drain can be installed at the base of the swale to direct water to a drywell or a community retention pond, or to a lower part of the site (Figure 4). While each site is unique, the following steps provide general guidance for constructing a swale to divert water away from the house (EPA 1999).
How to Construct a Swale
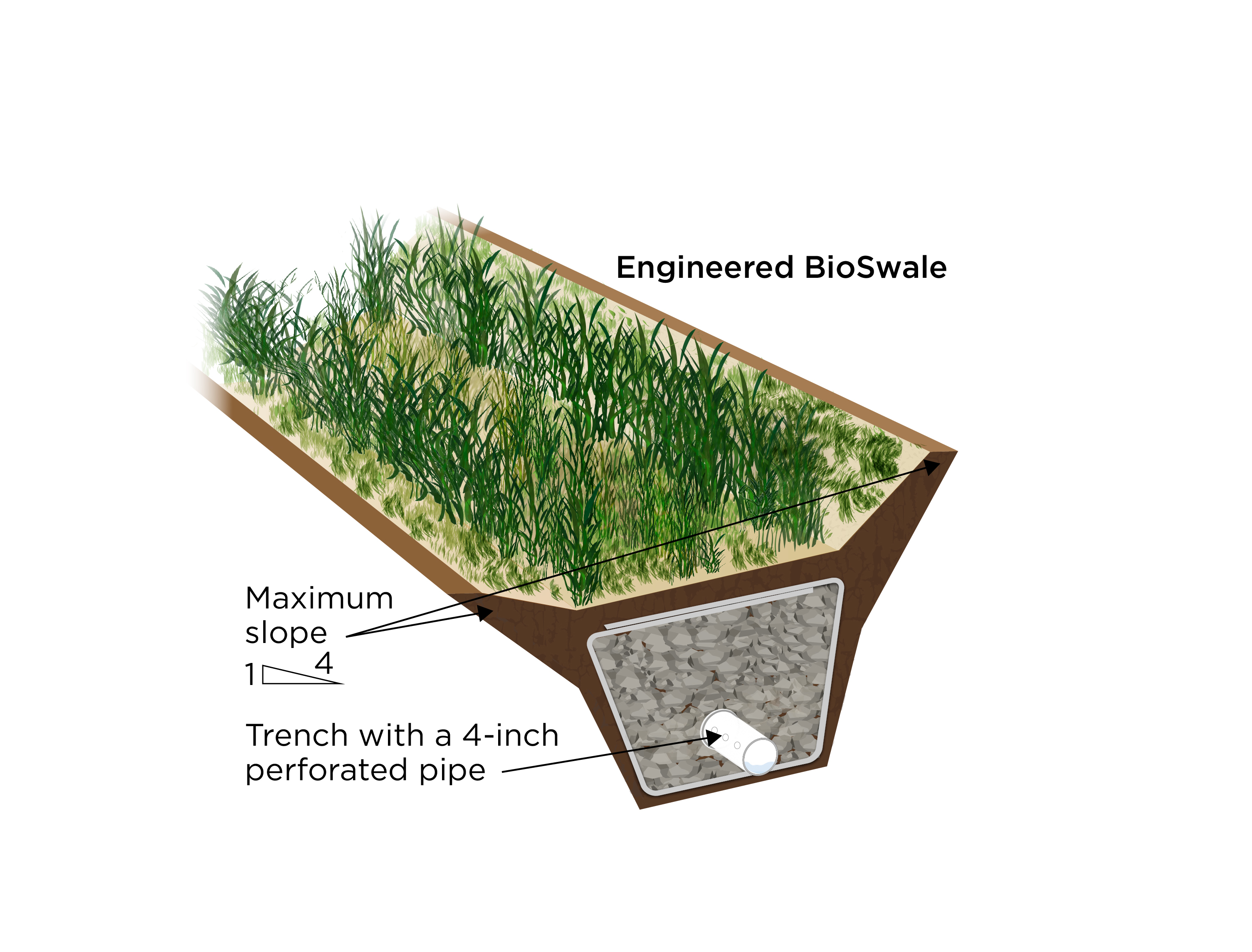
Drains
Drains can be installed to collect and direct surface water away from the foundation. Metal grated drains can be installed at the base of downward-sloped driveways or walkways. Drain pipe may be installed under pavers, stone, turf, or mulch at low points in the yard where drainage is needed to reduce surface ponding. This type of underground drainage is often referred to as a French drain (Figure 6 and Figure 7). It consists of a perforated pipe that is wrapped in rock and landscape fabric. The perforated pipe carries the collected stormwater to a lower part of the site or to a drywell for below-ground dispersal or off site to the stormwater sewer system or to a community retention pond. If the drain empties to daylight, it should terminate onto a sloped grade that directs water away from the building. A splash block or stones placed beneath the pipe opening or a sprinkler head to disperse outflow will help control erosion at this location (EPA 2012). Many communities have ordinances in place directing that stormwater be handled on site.
The French drain should be located 18 or more inches below ground and have a positive slope toward the drain outlet, which could be underground to a drywell, or a storm sewer, or to a downslope location on the site. Smooth PVC pipe is preferable to corrugated pipe, which is more likely to collect sediment and clog. See the following steps for constructing a French drain.
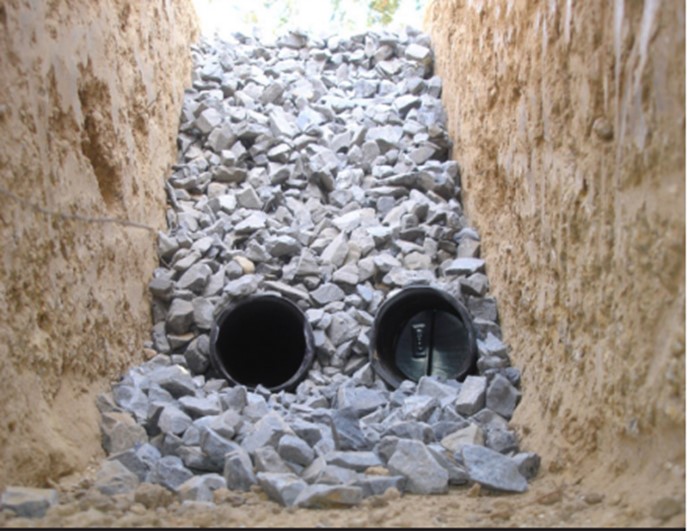
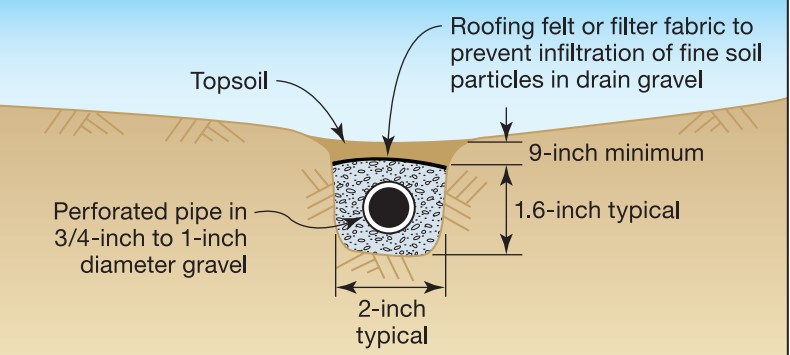

How to Install French Drains
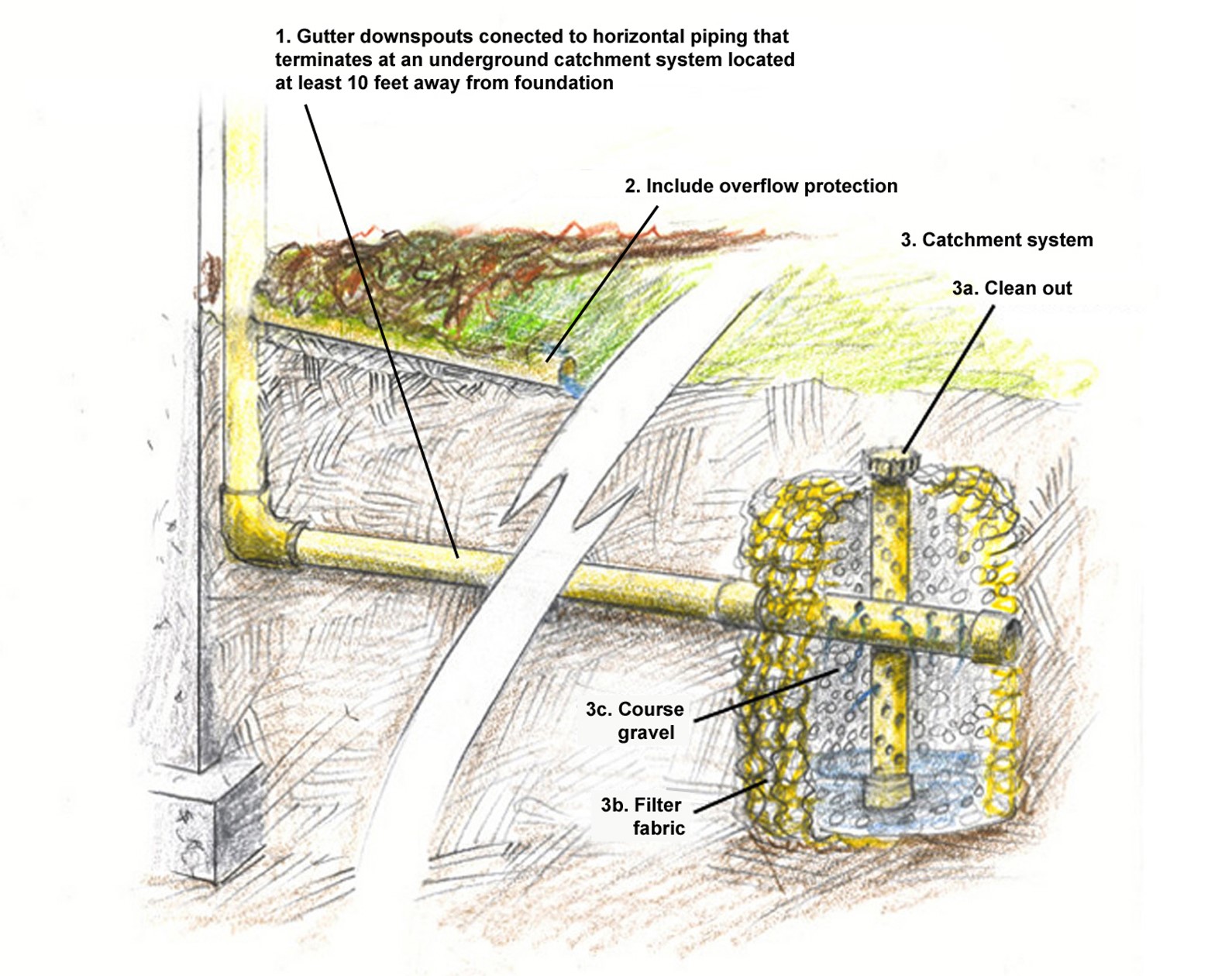 shown here used for downspout catchment, can also be used to receive water from a French drain." width="656" height="520" />
shown here used for downspout catchment, can also be used to receive water from a French drain." width="656" height="520" />
How to Install a Drywell
Follow local ordinances regarding stormwater runoff.